Avoid your inquiry is delay response, please enter your WhatsApp/WeChat/Skype along with the message, so we can contact you at the very first time
We will reply you within 24 hours. If for urgent case, please add WhatsApp: +8613188899036, or WeChat: 0531-87968777. Or call 0531-87968777 directly.
* We respect your confidentiality and all information are protected. We will only use your information to respond to your inquiry and will never send unsolicited emails or promotional messages.
Pipes burst. Valves stick. Staff rush across floors inside buildings. Downtime and water loss spiral. The fix is simple: a wireless LoRaWAN shut-off with a smart valve controller that acts fast, sends alerts, and keeps your system safe.
A LoRa smart valve is a remote wireless LoRaWAN shut-off and control device for HVAC, water supply, and industrial lines. It uses LoRa (long-range, low-power) radios to monitor and control flow, open/close the valve, trigger alarms, and run for years on batteries—even in deep-indoor locations.
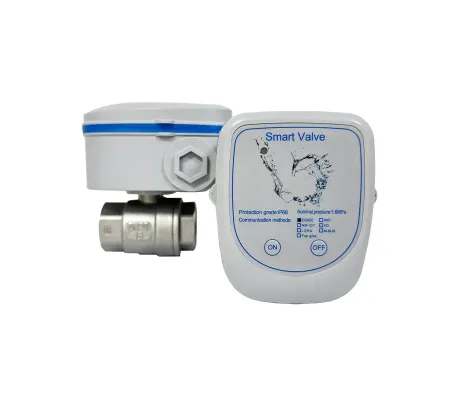

Think of it as a rugged endpoint that lives on your pipework and speaks LoRa. A smart valve is a remote actuator with sensing and a radio. Over LoRaWAN®, it signals through walls and equipment using wireless technology tuned for lora lpwan efficiency, not speed. Result: huge coverage with tiny power consumption.
In plain words: the device opens or closes the valve and reports state, alarms, and water flow trends to your building or plant system. Because it’s low-power, the valve can operate on batteries. That’s perfect where wiring is hard—roofs, basements, or remote yards. We offer a LoRaWAN smart lineup that drops into existing heating, cooling, and irrigation loops, and it integrates with common BMS/SCADA stacks.
One sentence summary you can reuse: a lorawan wireless smart valve delivers long-range control and telemetry with minimal maintenance.
Inside, you’ll find the actuator and driver stage plus inputs/outputs. Typical I/O includes 2x digital inputs, a 0-10VDC analog input, and command channels for opening and closing. The controller can take digital and analog signals from a sensor or PLC and push upstream reports so you can monitor and control the line.
From the software side, you configure each device to your network, set reporting periods (for ultra-low power consumption), choose ACK/retry behavior, and define alarm actions. Commands come from your gateway/network server down to the node. If you also need motion control, a companion LoRa rotary actuator can fit—see our LoRa rotary actuator for precision valve control.
You’ll see rapid wins in utility rooms and yards. Tie the node to a water meter to correlate water flow with actuation. In a water supply line, it can serve as a shut-off at the branch or main, and in irrigation it regulates zones without trenching power cables.
Many facilities combine the controller with a flow transmitter for batch fill, blow-down protection, or cooling-tower makeup. If you want measurement and isolation together, evaluate our smart flow meter & valve integrated device to simplify installation and commissioning.
LoRa’s gift is range. Expect extreme range links outdoors and exceptional deep indoor signal penetration in plants. Even with obstacles, it delivers exceptional obstacles penetration and reliable penetration across multiple floors inside buildings when you place gateways well. We routinely see gateways pick up nodes through steel and concrete.
For campuses, a handful of gateways cover wide footprints. For high-rise sites, stack gateways or remote antennas per fire zone or riser shafts. A well-planned RF survey ensures deep indoor coverage where you need it most.
The valve is a battery operated endpoint designed for ultra-low power duty cycles. Radios sleep, wake on schedule, and use short air-time packets. With efficient actuation, you’ll see long battery life on field deployments (often years battery life), even in cold rooms. Some projects aim for “years and through extreme long” maintenance intervals (to quote a field goal we hear often).
Below is a simple, illustrative power-budget view:
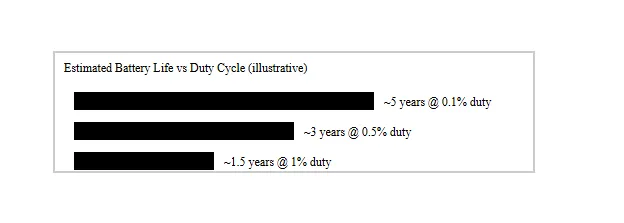
In short: plan for actuation frequency, ambient temperature, and uplink intervals. Batteries are field-replaceable; supercaps and DC feeds are options, too. Battery life depends on use, but design choices keep power consumption low.
LoRaWAN is an open protocol—specifically, we operate on the LoRaWAN open protocol wireless network. You might see it described as wireless LoRaWAN open protocol, which highlights interoperability. Devices join according to your LoRaWAN class; control nodes often run class C for fast downlinks when mains-powered, or Class A for battery endpoints. We also support LoRaWAN devices with ADR and confirmed messaging when needed.
Regulatory note: LoRa uses license-exempt bands. In Europe, you’ll see license free operation on EU868; other regions vary. For secure traffic, modern stacks do end-to-end AES encryption by default. If you prefer alternatives (Wi-Fi/Zigbee), see our Wi-Fi smart water valve option or compare the Zigbee smart valve for short-range meshes.
Tie the controller to a temperature and humidity sensor or a leak probe. When thresholds hit, you send an alarm that arrives as an alarm to your mobile, relayed mobile through the gateway, then forwarded by the gateway or the application server. The shut-off valve designed to work with leak logic can kill the main line stopping the leak. The valve can be turned off at the main, stopping the leak before major damage so no major damage is done.
Many teams also set counters for water budgeting. You’ll see phrases like “programmed for automatic shut-off based on counter:” or “shut-off based on counter value:” in config notes. Some systems even use automatic shut-off based on counter totals from a meter.
The LoRa ecosystem is broad. You’ll find notable brands like Milesight making sensors, and Strega producing specialized actuators. In vendor docs you might read: “discreet endpoint.the strega smart-valve:” followed by feature highlights, or “strega smart-valve can be programmed: … for water budgeting.”
Some literature mentions exclusive design with embedded radio/logic, marketing terms like strega smart, and model names such as the strega lora wireless smart valve (a lorawan wireless smart actuator), or even the exact line “lorawan wireless smart valve.” There are also nodes marketed as smart emitter endpoints for targeted actuation. We don’t endorse any single brand here—we support standards-based gear that you can mix and match.
Integration is straightforward. Typical field wiring lands on terminals for digital inputs and analog input (plus that 0-10VDC control everyone loves for drives and dampers). On the network side, you publish decoded payloads to MQTT/REST for the BMS, historian, or maintenance app. Many customers combine supervisory loops with valve control at the edge.
For tight flow control and balancing, pair your setup with a proportional regulating valve. It trims differential pressure and complements your LoRa endpoint for precise temperature and flow setpoints.
When in doubt, start on a pilot loop and expand outward. Your future self will thank you.
Key questions to ask your supplier:
Connectivity options (at a glance)
| Option | Range | Power | Notes | Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LoRa/LoRaWAN | Very long | Very low | Best for campus/plant scale; extreme range links | Our LoRaWAN smart valve lineup |
| Wi-Fi | Short | Moderate | Uses site WLAN; higher bandwidth | Wi-Fi smart water valve |
| Zigbee | Short/mesh | Low | Good for dense rooms | Zigbee smart valve |
Bonus: For actuation-first builds, you can also consider a stainless electric ball series as the isolation element (see our stainless electric options) while keeping LoRa control upstream.
A public campus added LoRa control to its domestic cold-water mains. Leak sensors under risers send an alarm to maintenance phones. The controller closes a shut off valve within seconds, turned off at the main, stopping the leak before major loss. Overflow is capped, and classes continue.
Telemetry drives reports on usage and trending. Pairing the controller with a building meter made batch fill smarter, and alerts route through the gateway or the application server to the CMMS. Staff liked that it worked through concrete and steel, citing exceptional deep indoor signal penetration.
Is LoRa “long enough” for my plant?
Usually, yes. With one or two gateways, you can cover large footprints and several floors. LoRa specializes in exceptional obstacles penetration and “hard-to-reach” spots.
Can it run on batteries?
Yes. The valve can operate on batteries for long periods thanks to ultra-low power design. Plan actuation counts and reporting to meet your target service intervals.
What happens during a leak?
Your sensor trips, devices send an alarm, and the shut-off action closes the valve. Alerts hit your phone via the app (the alarm to your mobile flows mobile through the gateway). The idea is main line stopping the leak so leak before major damage is caught before major damage is done.
Do you support EU and other regions?
We design for global ISM bands, including license free operation on eu868 in Europe. Ask about your local plan.
Can it integrate with my existing controls?
Yes—use the input terminals, analog channels, and digital inputs. Payloads integrate via APIs/MQTT to your BMS/SCADA.
How is security handled?
LoRaWAN uses 128-bit AES session keys, device keys, and secure joins. It’s part of the LoRaWAN open protocol standard and widely adopted.
| Feature | Typical Value |
|---|---|
| Radio | LoRa/LoRaWAN (lorawan wireless) |
| Controls | opening and closing commands |
| I/O | 2x digital inputs, one analog input (0–10 V) |
| Power | battery operated or external DC |
| Duty Cycle | Configurable (minutes to hours) |
| Range | Campus-scale; extreme range links outdoors |
| Sensors | Optional leak, humidity sensor, temperature |
| Enclosure | IP-rated for plant areas |
Marketing sheets sometimes use phrases verbatim. For clarity, here are typical snippets you may read in brochures or configuration notes (shown here for education and comparison):
We support interoperable, standards-based deployments whether you favor Milesight, Strega, or others.
From one smart-valve manufacturer to another engineer: we build to standards, test to failure, and ship fast. If you want help scoping your loop count, gateway plan, or payload map, tell us about your site and we’ll map a simple, reliable rollout.